OSHA Guidelines For PPE in Construction (2025)
The construction industry is filled with various hazards that pose a threat to workers’ safety. In order to minimize these risks, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth guidelines on the proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in construction sites. The document, available at, outlines the different types of PPE and their appropriate applications. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these guidelines to ensure worker safety and compliance with OSHA regulations.
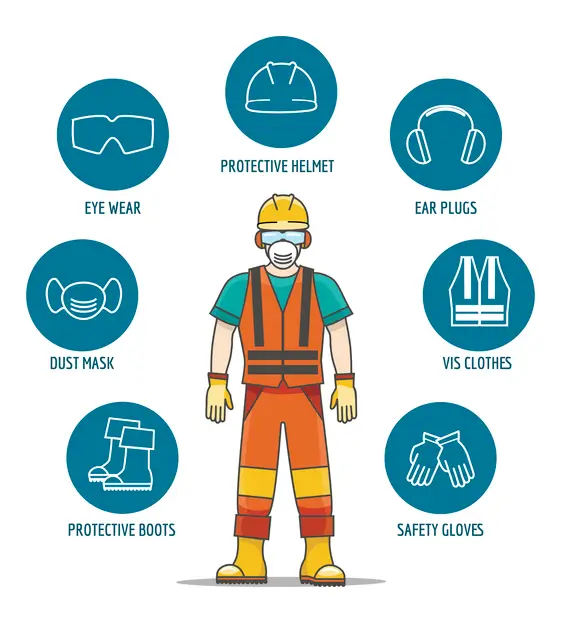
Types of PPE for Construction Workers


Head Protection To protect workers from head injuries, hard hats must be worn when there is a risk of falling objects, collisions, or contact with electrical hazards. Hard hats should be well-fitting, comfortable, and adjustable to accommodate various head sizes. They should also be inspected regularly for cracks, dents, or other signs of damage.

Eye and Face Protection Safety glasses, goggles, or face shields are essential to protect workers’ eyes from flying debris, chemicals, and other hazards. It is crucial to select the appropriate eye and face protection based on the specific job requirements, and workers should be trained on proper usage, cleaning, and storage.

Hearing Protection Workers exposed to high noise levels may need earplugs or earmuffs to prevent hearing damage. The type of hearing protection selected should depend on the noise levels and the worker’s comfort. It is crucial to train workers on the proper fitting and care of hearing protection equipment.

Respiratory Protection Respirators protect workers from inhaling hazardous substances like dust, fumes, or gases. Respirators should be chosen based on the type and level of hazard present and must be approved by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Workers should be trained on properly using, maintaining, and storing respirators.

Hearing Protection Workers exposed to high noise levels may need earplugs or earmuffs to prevent hearing damage. The type of hearing protection selected should depend on the noise levels and the worker’s comfort. It is crucial to train workers on the proper fitting and care of hearing protection equipment.

Respiratory Protection Respirators protect workers from inhaling hazardous substances like dust, fumes, or gases. Respirators should be chosen based on the type and level of hazard present and must be approved by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Workers should be trained on properly using, maintaining, and storing respirators.

Fall Protection equipment, such as harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points, is necessary for workers at heights of six feet or more above a lower level. It is crucial to select the appropriate fall protection system based on the specific work environment and train workers on its proper use, inspection, and maintenance.
Implementing a Successful PPE Program

Perform a hazard assessment to identify the types of PPE required for specific tasks.

Select appropriate PPE based on the hazard assessment and ensure it is correctly fitted and comfortable for workers.
Train workers on the proper use, care, and maintenance of safety gear through online PPE overview training courses.

Inspect and maintain PPE regularly to ensure its effectiveness.

Create and enforce policies for PPE use on the construction site.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing OSHA guidelines on Personal Protective Equipment for construction workers is essential to ensure their safety and compliance with regulations. By providing the appropriate PPE, training workers on its use, and enforcing policies, employers can significantly reduce the risk of injury and promote a safe work environment.





