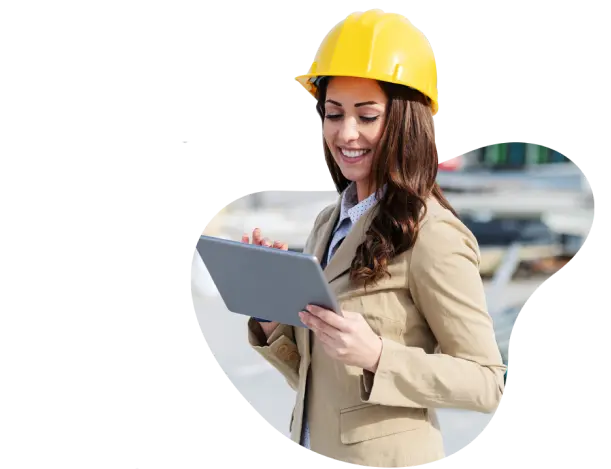
Confidentiality, Intellectual Property Protection, and Information Security
Why Workers Choose Us
| features |  |
other providers |
|---|---|---|
| Instant Downloadable Certificate | ||
Free Study Guide
|
||
Discounts For Businesses
|
||
| No Hidden Cost | ||
Mobile Compatibility
|
||
Flexible Learning
|
Satisfied Customers
Learning Objectives
- Recognize what information is considered sensitive.
- Recognize if you are dealing with it.
- Identify the ways you can protect sensitive information and intellectual property, including how to respond to a request by a third party for this information.
Course Outline
-
1. Overview
- About this course…
-
2. Definition
- Sensitive Information
- General Examples
- Specific Examples
- Intellectual Property
- Trade Secrets
-
3. Legal Protection
- Trade Secrets Legislation
- Confidentiality Policies and Agreements
-
4. Company Protection
- Discreet Handling
- Third Parties
- Presentations
-
5. Responses
- Protect Company Details
- Recommendations
- Case Study — GM vs. Volkswagen
-
6. Conclusion
- Conclusion
Group Discount for Corporate Accounts

VIDEO TESTIMONIAL
FAQ
How long does it take to complete the Confidentiality, Intellectual Property Protection, and Information Security course?
Are there any prerequisites for enrolling in the Data Security Training?
Can I access the course materials after completing the Intellectual Property Protection Course?
What topics are covered in the Confidentiality and Information Security Workshop?
Is certification available upon completing the Online Training: Protecting Intellectual Property?
Join our mailing list
Get announcements, industry updates and promotional offers.
17350 TX-249 Ste 220 19204, Houston, TX 77064, United States

