
New York OSHA 10-Hour General Industry
$59 $89.00


Enroll Now
New York OSHA 10-Hour General Industry
$59
$89.00
Why Workers Choose Us
Free Study Guide
Access to quality material
One Free Course
Enjoy bonus learning
No Hidden Cost
Transparent pricing only
Professional Support
24/7 customer assistance
Who Should Take NY OSHA Course for General Industry?
- Retail and service jobs: Perfect for employees who interact with the public and need to recognize and prevent common workplace hazards.
- Healthcare facilities and nursing homes: Designed for healthcare staff who must maintain a safe environment for both patients and coworkers.
- Warehouses and manufacturing plants: Ideal for workers who handle equipment or materials and need to stay compliant with OSHA safety standards.
What You Will Learn
In the OSHA 10-Hour General Industry course, you will learn the fundamental safety practices every general industry worker needs.
Course Outline
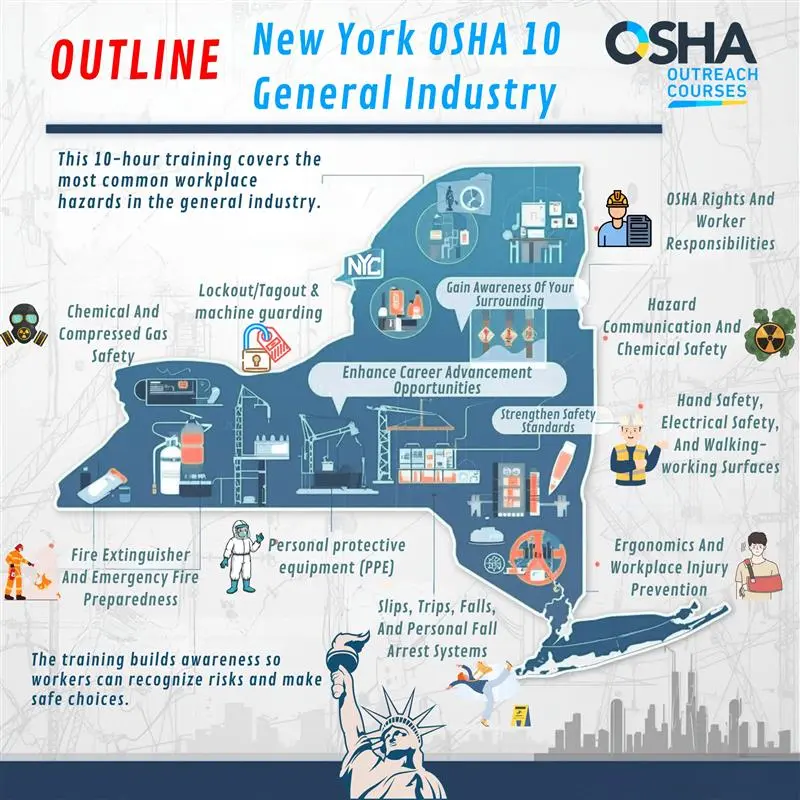
How Does The Online Program Work?
Cost of OSHA 10-Hour NY General Outreach Training Course
The OSHA NY 10-Hour General Industry course typically costs between $99 and $159, depending on the provider. While some training platforms may offer discounts or flexible payment options, it’s important to be cautious of “free” OSHA 10 courses, as they are often not OSHA-authorized or accredited. For your convenience, you can choose to pay through AfterPay, which allows you to split the total cost into four manageable installments. To learn about current discounts or promotions, contact our support team via live chat.
Group Discount for Corporate Accounts

How to Enroll in New York OSHA 10-Hour General Industry
1
Choose an authentic course provider.
2
Complete the registration process & pay for the course.
3
Start your training program from the first module.
4
Finish all the modules and pass the exam.
Benefits of Online NY OSHA General Industry Course
This course is self-paced and completely online for workers.
- Self-paced and mobile-friendly.
- Start anytime, from anywhere.
- Receive an official DOL OSHA 10 wallet card, valid nationwide.
What You Will Get
Upon completing this program, you will receive verified credentials that validate your training, provide official proof of completion, and award continuing education units (CEUs).
OSHA 10 DOL Card
Once you successfully complete the course, you will receive a plastic 10-Hour DOL card from the U.S. Department of Labor. This official card will be mailed to your address within six to eight weeks of course completion. Each card includes a unique QR code that enables employers to instantly verify its authenticity. Holding an NY OSHA DOL card confirms you have authorized training and makes you eligible for employment with numerous New York employers.
Updated Safety Knowledge
The course equips workers with comprehensive knowledge of OSHA regulations and risk control methods. Trainees learn to recognize workplace hazards, implement preventative measures, and promote a culture of safety across their organization.
Certificate of Completion
After finishing the course and passing the final exam, you can immediately download and print your Certificate of Completion as evidence of your training. This certificate confirms that you’ve completed an OSHA-authorized course, but it should not be mistaken for an official OSHA certification, as OSHA itself does not issue certifications.
Guide To New York OSHA 10-Hour General Industry

How to Get Your OSHA DOL Card in New York
Enroll in an OSHA-authorized course
Provide your US address
Pass the quizzes and final exam
Wait for DOL to issue your plastic card
Receive the card at your doorstep
DOL cards are delivered within 6-8 weeks after you have completed the course.
FAQs
In New York, it is recommended to renew this training every 5 years.
If you lose your card, you can request a replacement through the training provider. Our agents are always ready to assist you in this matter. Please note that you may be asked a small fee for the replacement card.
Yes. New York is an OSHA state, but it has its own state-run occupational safety and health program. New York operates a State Plan under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) framework. This means that while federal OSHA regulations apply, New York has its own state-specific regulations and enforcement mechanisms through the New York State Department of Labor's Division of Safety and Health.
In New York, general industry workers are recommended to complete the OSHA 10-hour General Industry training within 90 days of starting their job.
If you buy multiple courses in this category, you will get a group discount. In case you’re only buying a single course, you can check with our representative to find out if any individual discounts or promotional offers are available.
Yes, the courses are provided by UL Solutions (PureSafety), which an authorized provider of OSHA outreach training.
Yes, if you start this course and don't complete it within the next 180 days by passing the final quiz, this course would expire. In that case, you would need to repurchase this program.
According to OSHA, General Industry refers to workplaces that are not part of the construction, agriculture, or maritime sectors. It covers a wide range of industries such as manufacturing, warehousing, healthcare, and retail.
Additional Resources
- Our States Guide
- General Industry Standards
- Scholarship
- Practice Test
- OSHA Outreach Training Program
- OSHA 29 CFR
About OSHAOutreachCourses.com
Since 2015, OSHAOutreachCourses.com has helped thousands of New York workers complete OSHA-authorized Outreach training.
Join our mailing list
Get announcements, industry updates, and promotional offers.

