The construction industry continues to report the highest number of fall-related fatalities in the United States. Each year, more than 300 workers die from falls, accounting for about 20% of all occupational deaths (source: OSHA, 2024).
Falls are preventable, yet they remain one of the most common causes of serious workplace injuries. Implementing a fall protection program that includes hazard identification, training, and equipment safety is essential for saving lives and avoiding costly violations.
Understanding Fall Protection Training
Fall Protection Training is a key component of both the OSHA 10-hour and 30-hour Construction courses, which teach workers how to identify and prevent fall hazards effectively.
Through OSHA’s training programs, workers and supervisors learn about:
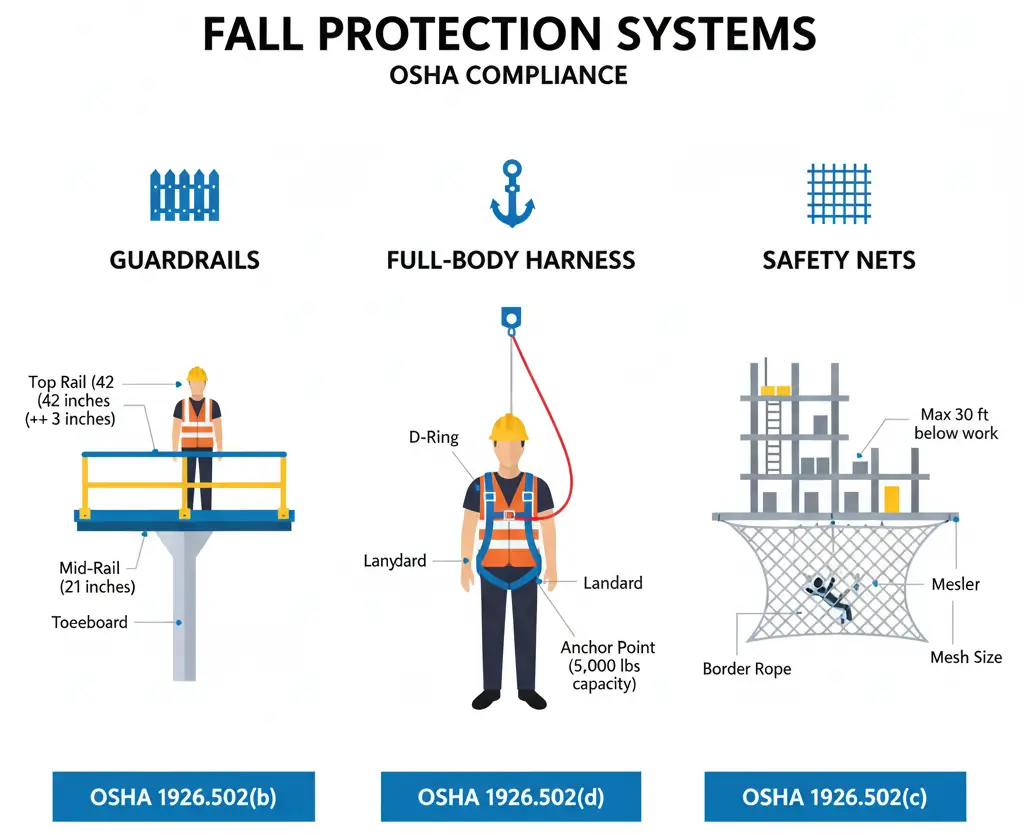
Guardrail systems and safety nets
Personal fall arrest systems (PFAS)
Proper inspection and use of fall protection equipment
Safe work practices on elevated surfaces
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), falls are the second leading cause of workplace deaths, responsible for 15% of all fatalities in 2023 (source: BLS Workplace Injuries Report 2023).
OSHA Fall Protection Standards
OSHA mandates employers to provide fall protection at specific height levels depending on the industry:
General Industry: 4 feet
Shipyards: 5 feet
Construction: 6 feet
Longshoring operations: 8 feet
Employers must ensure that workers are protected from falling off platforms, elevated workstations, floor openings, and ladders.
Additionally, OSHA requires a fall protection plan when working near heavy equipment, hazardous materials, or open-sided platforms.
Essential Components of Fall Protection
1. Guardrails and Handrails
Must be 42 inches high, with a mid-rail at 21 inches.
Should be securely attached to walls or posts.
2. Toe Boards
Prevent tools and debris from falling.
Must be installed around elevated work areas with a maximum ¼-inch gap from the floor.
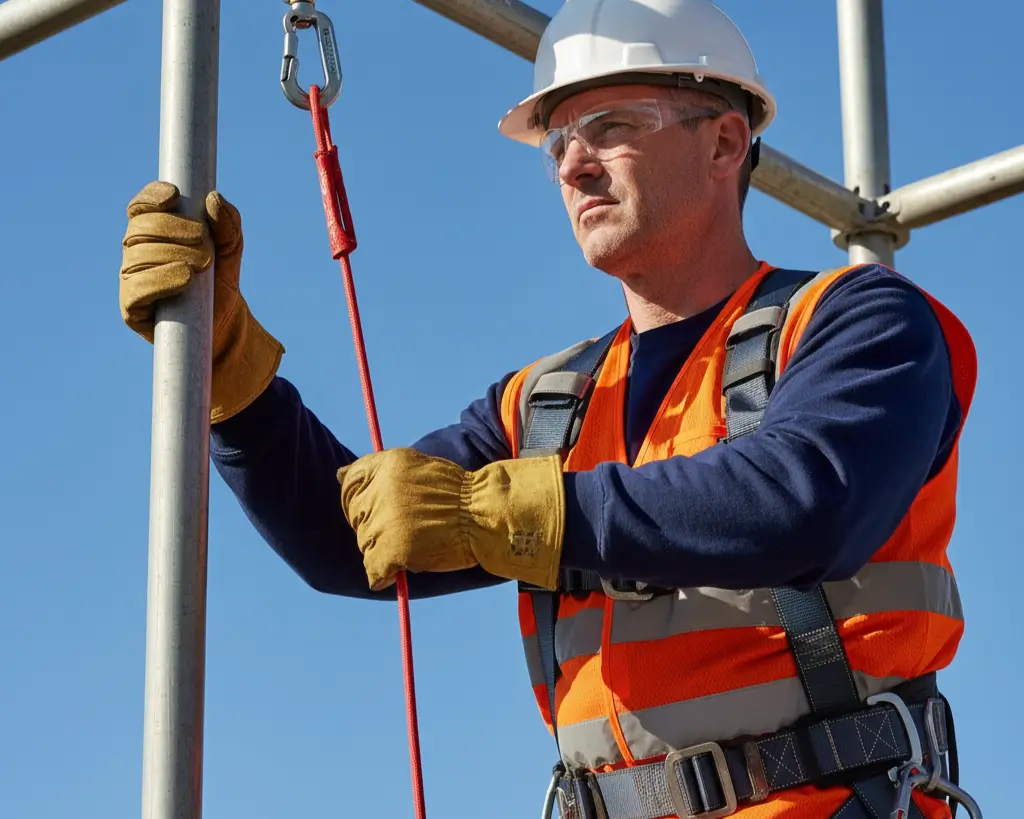
3. Full-Body Harness and Lanyards
Must be properly fitted and inspected before use.
Keeps workers suspended safely in case of a fall.
4. Safety Nets
Required when working at heights of 25 feet or more where guardrails are not feasible.
5. Proper Scaffolding
Scaffolds over 10 feet high must have guardrails and be inspected by a competent person.
Workers on suspended scaffolds must be anchored to an independent lifeline.
Preventive Measures for Fall Protection
To minimize fall-related risks, employers should take the following proactive steps:
Conduct Daily Safety Briefings – Discuss site conditions, slippery surfaces, and elevation risks.
Use Warning Lines and Control Zones – Limit worker access to high-risk areas.
Regular Equipment Inspections – Ensure harnesses, anchors, and lifelines are maintained.
Provide Proper Training – Workers must be trained to use fall protection systems correctly.
Create a Written Fall Protection Plan – Document hazard assessments and rescue procedures.
OSHA 10- and 30-Hour Construction Training
Both OSHA 10-Hour and OSHA 30-Hour Construction Training courses cover fall protection in depth.
The OSHA 10-Hour Course provides basic safety knowledge for entry-level workers.
The OSHA 30-Hour Course is designed for supervisors and managers, covering advanced topics such as:
OSHA Outreach Courses Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Site-specific safety plans
Upon completion, workers receive an OSHA DOL card, recognized nationwide as proof of safety training adherence.
👉 Enroll today in an OSHA 30 Construction Course to strengthen your fall protection knowledge and reduce workplace accidents:
Enroll Now in OSHA Outreach Courses

Statistics on Fall Hazards
300+ construction workers die annually due to falls (OSHA Data, 2024).
15% of all workplace fatalities result from fall incidents (BLS CFOI, 2023).
57% of ladder-related fatalities occur in the construction industry (CDC, 2022).
These statistics highlight the urgent need for comprehensive fall protection programs and consistent OSHA training.
Conclusion
Fall protection isn’t optional – it’s a legal and moral responsibility. Simple measures such as ensuring guardrails are in place, workers wear proper harnesses, and daily site checks are performed can save lives.
By complying with OSHA standards and promoting continuous safety training, construction companies can prevent tragedies, improve productivity, and avoid severe penalties.
👉 Take proactive steps now. Get OSHA-authorized training and build a safer workplace for every worker.










