Workplace accidents, illnesses, and medical emergencies can happen anytime. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), over 4.6 million workplace injuries occur annually in the U.S. Employers must have an effective first aid program in place to protect employees and improve survival rates during emergencies.
This article explains the basics of OSHA’s First Aid Program, including training, inventory, AEDs, and triage – the foundation of workplace health and safety.
What Is OSHA’s First Aid Program?
OSHA’s first aid program requirements ensure organizations plan for illnesses, injuries, and fatalities at work. After employees complete OSHA 301 forms, employers can identify their workplace first-aid needs.
A critical requirement is calculating Emergency Medical Services (EMS) response times for each location. Ideally, EMS should arrive within 8 minutes or less. For high-risk environments, advanced EMS response should be under 4 minutes.
Employers must:
Coordinate with local fire and rescue services
Put first aid guidelines and policies in writing
Communicate program details in languages employees understand
Three First Aid Basics Employers Must Implement
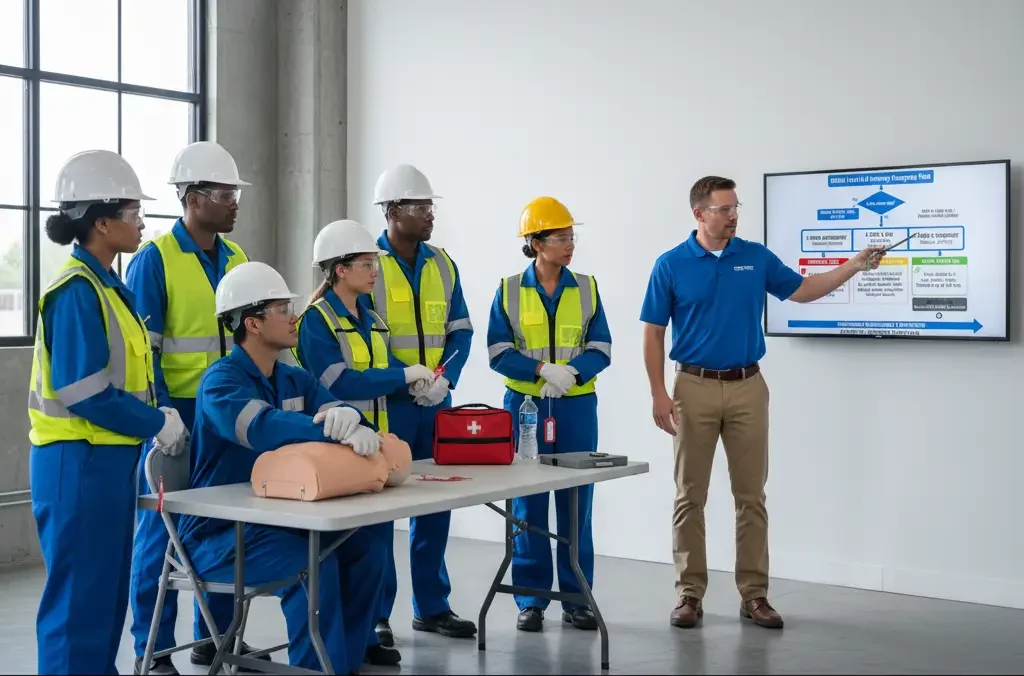
1. Appoint and Train First Aid Providers
Organizations should designate employees to receive OSHA-authorized first aid training. This includes CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation), since heart attacks are among the most common workplace emergencies.
Fact: Every year, nearly 436,000 Americans die from cardiac arrest (American Heart Association). Early CPR can double or triple survival rates.
2. Maintain a First Aid Inventory
Employers must assign someone responsible for medical supplies, checking stock, and replacing expired items. Supplies should be:
Adequate for the workforce size
Easily accessible in emergencies
Inclusive of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
3. Train Employees on AED Use
AEDs have become more effective, portable, and easy to use. Survival rates increase significantly when defibrillation occurs within 3-4 minutes. CPR is vital until an AED is available. Every workplace should have trained AED responders to manage sudden cardiac arrests.
Understanding Triage in the Workplace
Triage is the process of evaluating and prioritizing patients during emergencies. Without proper knowledge, responders may misjudge the severity of injuries. Training ensures employees:
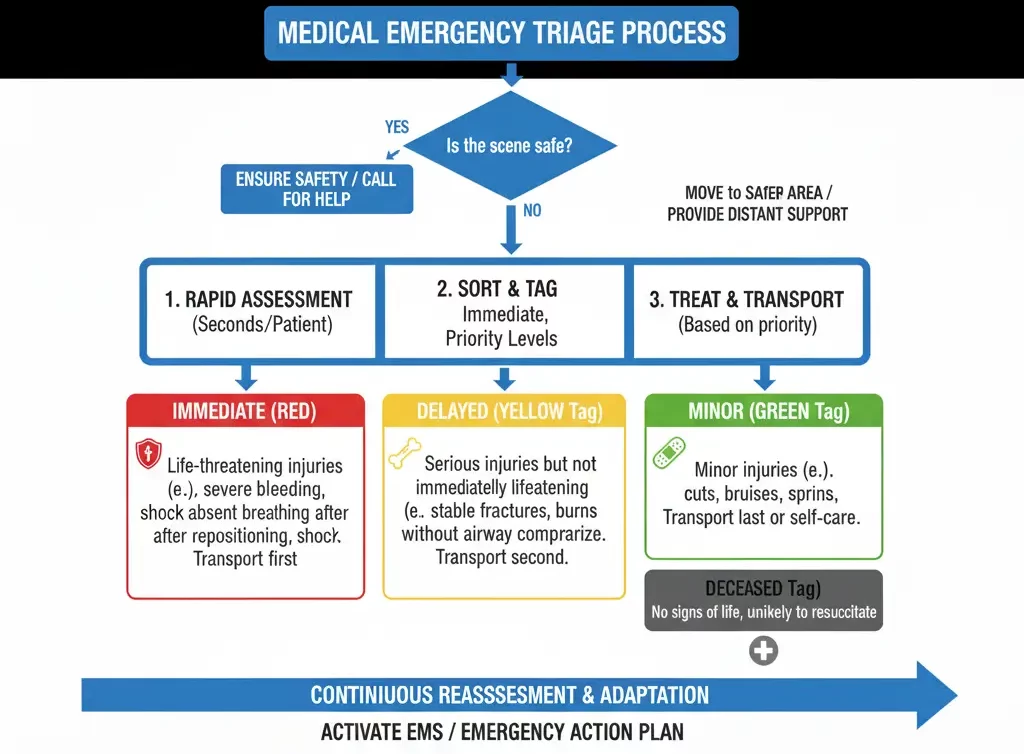
Recognize life-threatening conditions
Provide immediate care while awaiting EMS
Reduce panic and act with confidence
📌 OSHA strongly recommends calling 911 immediately for professional assistance in any life-threatening scenario.
Why Workplace First Aid Programs Matter
According to OSHA, effective first aid programs reduce workplace fatalities and injuries by 25-30%. Benefits include:
Faster response during medical incidents
Improved employee confidence and morale
Adherence with OSHA standards
Reduced downtime and legal risks for employers
For more on workplace safety, see our internal guide on Emergency Preparedness in the Workplace and our blog on OSHA Outreach Courses.
Conclusion
Implementing first aid basics is essential for protecting workers. Employers should:
Provide first aid and CPR training
Maintain an up-to-date medical inventory
Equip workplaces with AEDs
Train employees in triage procedures
By following OSHA guidelines and fostering a culture of safety, organizations can significantly improve emergency response outcomes and safeguard their workforce.










